

Endovascular intervention has quietly revolutionized how we treat blood vessel problems. Instead of large open incisions, today’s specialists often navigate miniature catheters and stents through the body’s natural “highways,” fixing problems from the inside out. In this guide, we’ll walk you through every major aspect of endovascular intervention procedures, what they are, how they work, who needs them, and what recovery really looks like.
By the end, you’ll know exactly why this minimally invasive field is growing 10%-plus each year and why we at SurgeonsLab are so passionate about it.
Endovascular intervention is a group of minimally invasive, image-guided procedures performed inside (endo) the blood vessels (vascular). interventional radiologists thread catheters through small skin punctures, often at the groin or wrist, then deploy balloons, stents, coils, or medication precisely where they’re needed.
Open aortic repair involves opening the chest or abdomen and clamping the aorta. Mortality rates hovered near 5%. Modern endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) cuts that to about 1.2% in the first 30 days while slashing hospital time by 4 days on average.
By 2030, 1 in 6 people will be over 60. Aortic aneurysms, PAD, and carotid disease all rise with age, driving demand for gentler options.
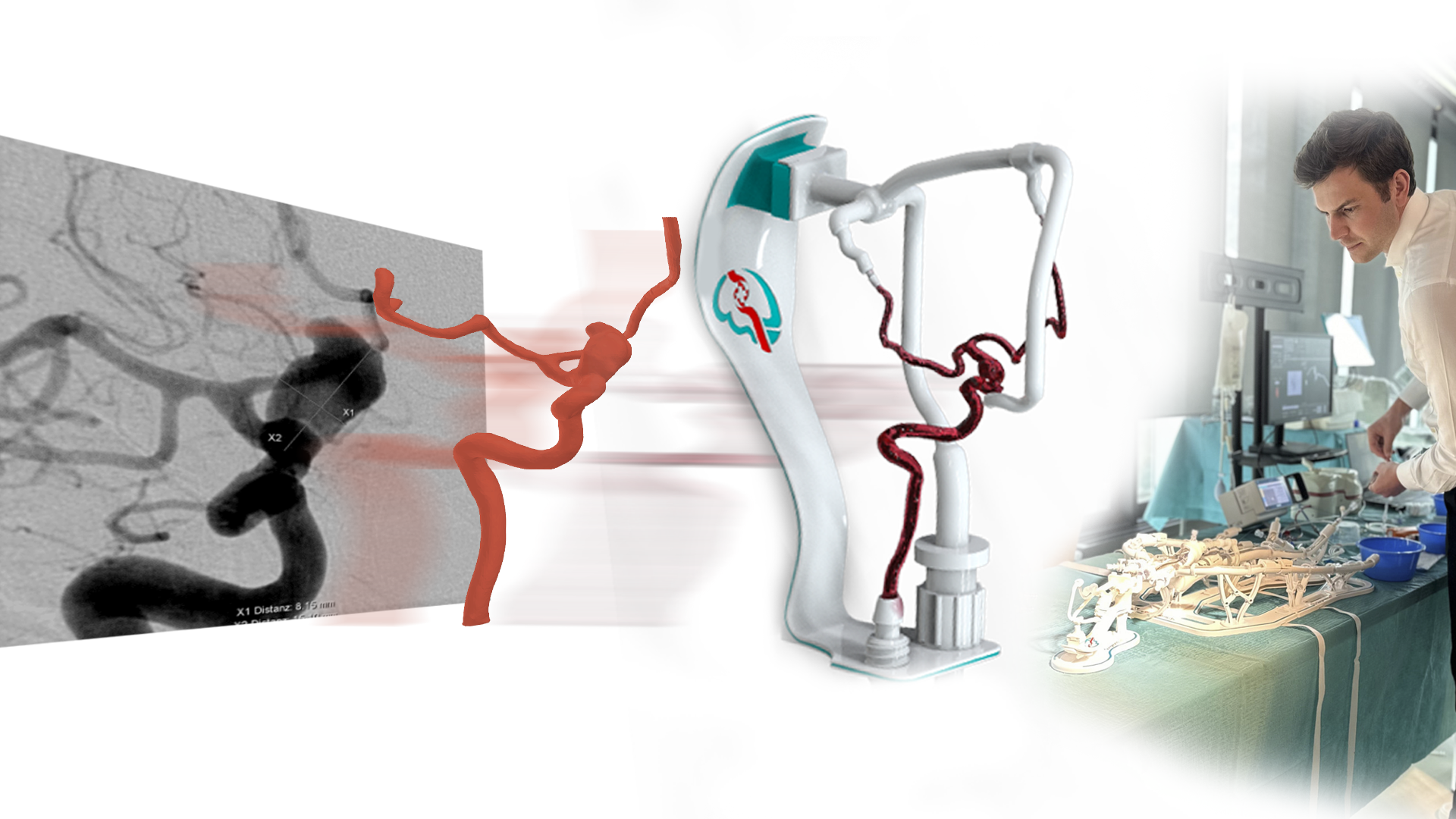
High-definition fluoroscopy, 3-D road mapping, and even fiber-optic shape-sensing catheters enable millimeter-level accuracy. Robotics may soon let interventional radiologists operate from another room or another city while avoiding X-ray exposure.
Step-by-Step: What Happens During an endovascular intervention
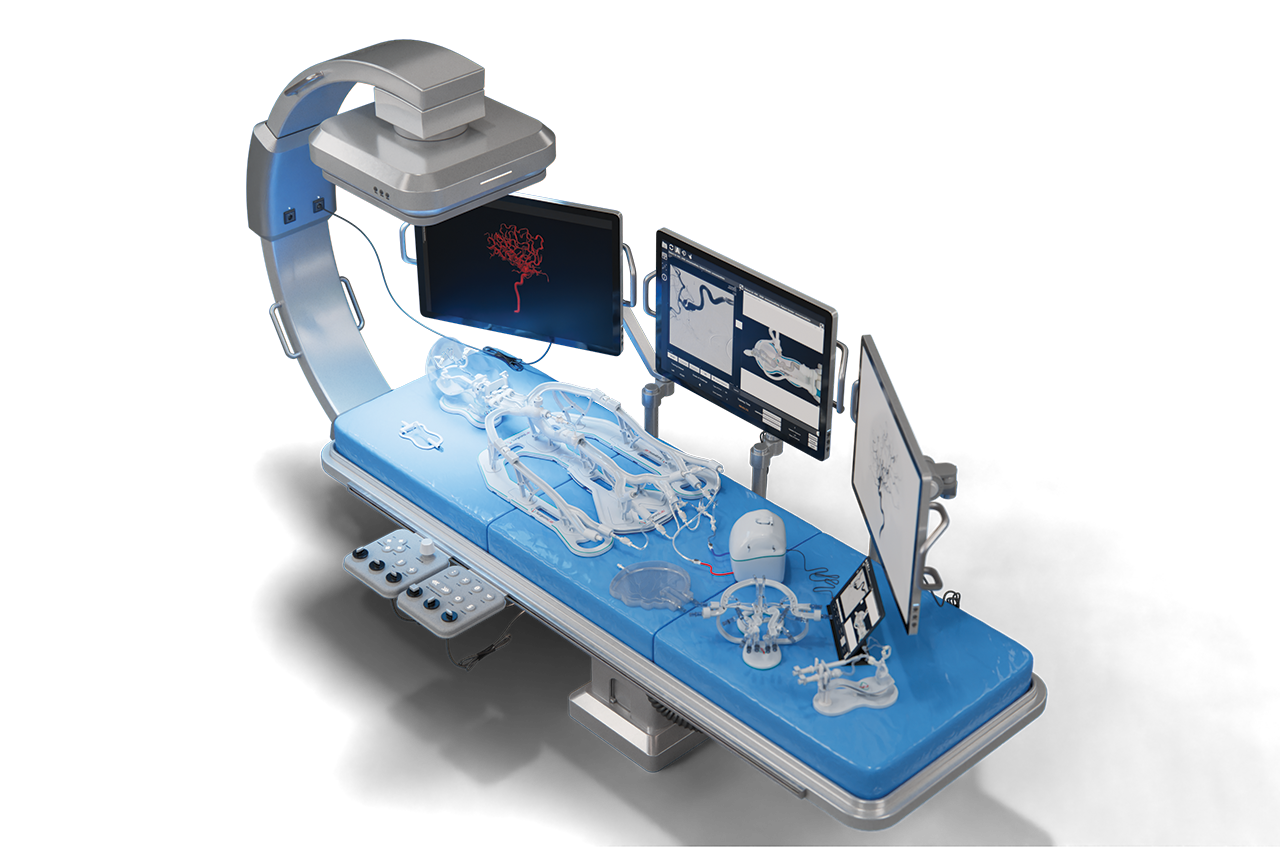
You’ll likely have a CTA or MRA scan. Our team at SurgeonsLab often uses 3-D printed simulators (see our Interventional Radiology Simulator collection) so interventional radiologists can practice on a patient-specific replica beforehand, cutting procedure time and X-ray dose.
After numbing the skin, we place a needle into an artery (femoral or radial). A sheath is introduced, and contrast dye lets us steer under live X-ray.
Depending on the goal, the surgeon may:
Tiny plugs or a simple pressure seal the puncture. No large sutures are needed.
Most patients walk within hours. Discharge is often the next day, with light activity for a week.
Overall: major complication rates are lower than comparable open surgeries across almost every category.
Endovascular options suit many but not all patients. Key factors we evaluate at SurgeonsLab include:
Robotic catheter platforms already allow operators to sit behind a lead-lined console, cutting radiation by 95% and reducing hand fatigue. Artificial intelligence road mapping promises real-time vessel reconstruction without dye, reducing kidney risk. SurgeonLab’s simulators help train clinicians on these emerging tools before they reach your hospital.

Modern devices have 20-year durability data with > 90% freedom from fracture.
No. Nitinol and PTFE materials are MRI-compatible and rarely trigger detectors.
Yes. Medicare and major insurers cover FDA-approved EVAR, carotid stenting, thrombectomy, and most PAD interventions.
Almost always. Your clinician will provide device-specific guidelines, but most grafts are MRI-safe up to 3 T.
Endovascular intervention procedures are changing the landscape of vascular care, offering less invasive treatment, faster recovery, and strong outcomes for patients worldwide. At SurgeonsLab, our mission is to empower medical professionals and trainees with advanced simulation tools like our interventional radiology simulator to help them master these innovative techniques safely and effectively.
If you’re interested in enhancing your endovascular skills or want to explore our educational solutions, visit our interventional radiology simulator page or browse our full collection. Let SurgeonsLab support your journey in advancing patient care and medical education.

Subscribe to our newsletter and be the first to access exclusive content and expert insights.